Watch: a unique heavenly light episode that dazzles the astronomers
From time to time, the Hubble Telescope of the European Space (ISA) and the American (NASA) can take an exceptional picture of the deep universe, this time - on the ninth of August this time - the researchers of this telescope released a new image of a ring of light in which two galaxies share with QuazarBright.
Shiny points
In the picture, you can notice 4 points of light that rises around two bright, overlapping criminals, these two trees are two huge galaxies that move away from the ground 4 billion light years, meaning that if you now decide to travel there at a speed of light (300 thousand kilometers per second) you will reachThere are 4 billion years after.
As for the ring of light and its four points, they are the exceptional in the matter, as these points are repeated images of the same crime, and it is a Kwizar called 2m1310-1714, discovered 3 years ago and since its discovery and is the focus of the attention of many astronomers.
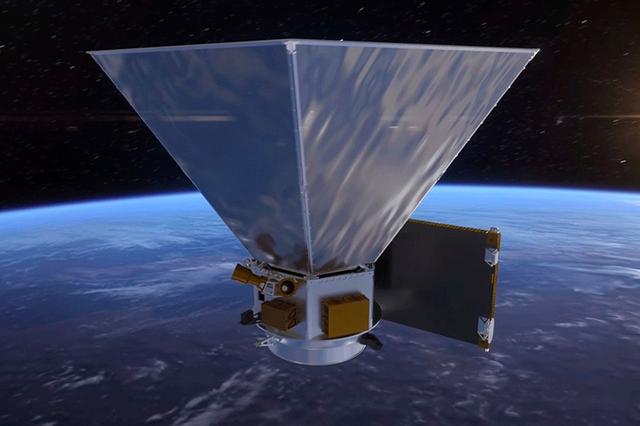

And the camers are the nuclei of galaxies very far with a very active heart, and because of its extreme dimension, we do not see from the body of the galaxy except this active heart..
Gravity lens
But to understand the reason for the repetition of the pictures of this kwazar about galaxies, we can start from the theory of Albert Einstein's relative theory that says that light does not always go in straight lines, but rather bends of the gravity of heavenly bodies, and in 1919 the English astronomer Arthur Edington managed to prove this.
Edington photographed the position of a group of stars with the sky in two cases, the normal state (sky at night) and the state of the total eclipse (while the sun is between these stars but it is blocked by the moon and the stars can be monitored).The results showed that the presence of the sun changed from the sites of those stars, which means that the light of those stars that connect us on the earth bent over the presence of the sun.
The same is happening in the case of the kwazar 2M1310-1714, as it falls on the ground in the background of the two galaxies, at a distance of more than 10 billion light years, and while the light rays coming from it crosses the two galaxies, they bend their way to us, due to the attractiveness of the two galaxies, which causes thisBeduch visual deformation.
This phenomenon is called gravitational lensing, because what gravity does from deformation in the light is similar to what the glass lenses do, and this is not the first time that Hubble lenses have taken such rings.LRG) It is about 3 billion light years away from us, flying around another galaxy.
Hubble cameras
The new image was taken by the WFC3 camera, which, since its installation in 2009, has been greatly captured by the Hubble telescope, it provides a wider vision and a larger scope of wavelengths, which means greater accuracy compared to other cameras in the telescope itself.
Although her practical age was only 3 years, this camera is still able to dazzle scientists and the public alike, so far.